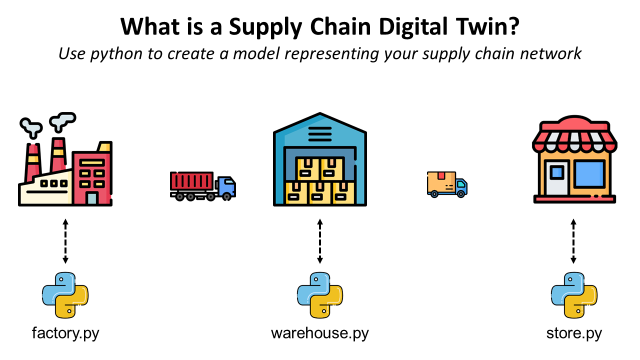
What Is a Supply Chain Digital Twin?
Use python to create a model representing your supply chain network to optimize your operations and support strategic decisions.
Article originally published on medium.
A digital twin is a digital replica of a physical object or system.
A Supply Chain digital twin is a computer model that represents various components and processes involved in the supply chain such as warehouses, transportation networks, and production facilities.

In previous articles, I shared examples of python models designed for specific applications such as transportation routing optimization, supply chain network design or production planning.
In this article, we will try to take a step back and build a Supply Chain Digital Twin representing your complete end-to-end operations from production to store delivery.
💌 New articles straight in your inbox for free: Newsletter
What is a Supply Chain Digital Twin?
A goal-oriented network
A supply chain is a goal-oriented network of processes and stock points used to deliver goods and services to customers.
To create a digital twin of a supply chain using Python, you would first need to define the various components and processes that make up the supply chain.

This could involve creating data structures to represent warehouses, transportation operations, and production facilities and defining the relationships between these components.
Data & parameters
Next, you would need to collect data on the various components and processes of the supply chain, such as
- locations and capacities of warehouses
- routes and capacities of transportation networks
- production rates of production facilities
- customer and store demand

This data could be stored in databases or other data storage systems or directly connected to your warehouse management systems and ERP.
Simulation blocks
Once you have the data on the supply chain components and processes, you can use Python to create algorithms and simulations that replicate the behaviour of the supply chain.
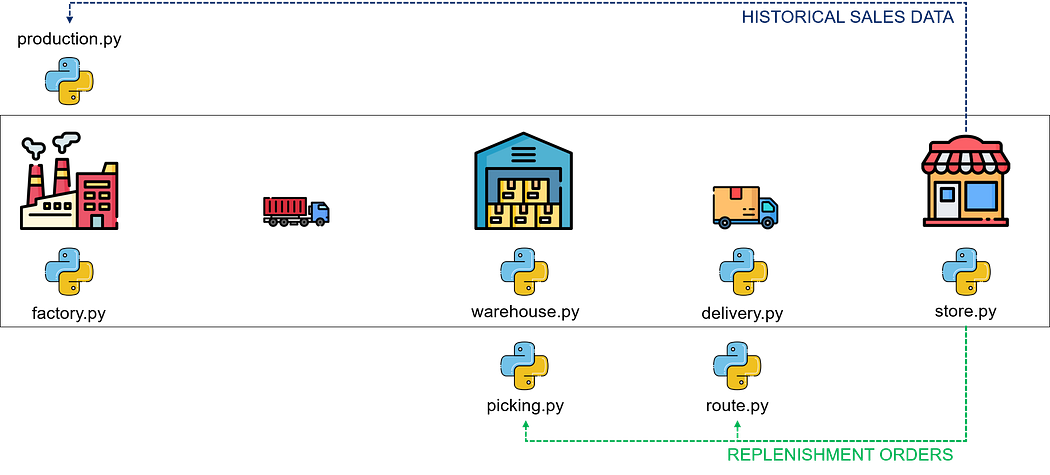
This could involve using optimization algorithms to
- determine the most efficient routes (output) to deliver stores using replenishment orders (input) coming from the store model
- improve the picking processes (output) in your warehouse to prepare stores replenishment orders (input)
- schedule your production (output) based on demand forecasts built with the stores’ sales historical data (input)
Examples of building blocks
Overall, creating a supply chain digital twin with Python would involve a combination of data collection and analysis, algorithm development, and simulation modelling.
It would likely require a deep understanding of supply chain management and experience with Python programming.
Let us take three examples of elementary blocks built with Python.
How to simulate warehouse operations?
We define a warehouse class as one that has attributes for the warehouse’s location, capacity, and inventory.
The add_inventory and remove_inventory methods can add and remove items from the warehouse’s inventory, respectively.
This is a simple example, you can add additional attributes and methods by considering processes productivity, warehouse costs structure, workforce management or picking processes to improve the model.
How to simulate road transportation?
We define a Truck class that has attributes for the truck’s location, capacity, and load.
The move_to method can be used to move the truck to a new location, and the load_cargo and unload_cargo methods can be used to load and unload cargo, respectively.
The solution above can be improved by adding loading and unloading times, timestamps for lead time calculations, costing parameters, or detailing the handling units (pallets, cartons, …).
How to simulate store inventory management?
We define a Store class that has attributes for the store’s location and inventory.
The place_order method can be used to place an order for a given item and quantity.
- If the store has enough of the item in inventory, the order will be fulfilled, and the inventory will be updated accordingly.
- Otherwise, an error message will be printed.
You can improve it by adding the requested delivery date and managing several handling units, including the outbound sales and lead times.
Next Steps
Connect the blocks
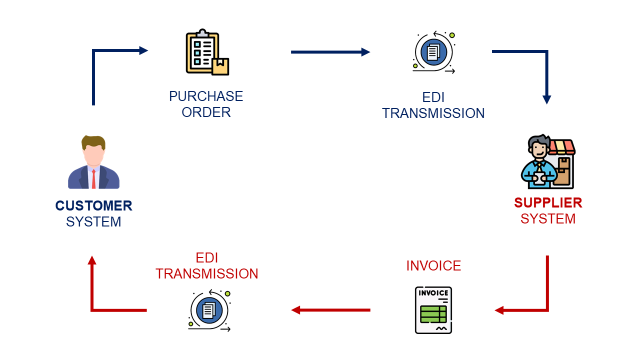
Now that you have built your elementary independent blocks, you need to connect them:
- Your store is sending replenishment orders to the warehouse management system using the ERP.
- Your warehouse prepares the orders, packs the items and puts them on pallets.
- Pallets are loaded in a truck
- The truck delivers the pallets to the store
And add external parameters such as customer demand or raw materials supply constraints.
Supply Chain Analytics
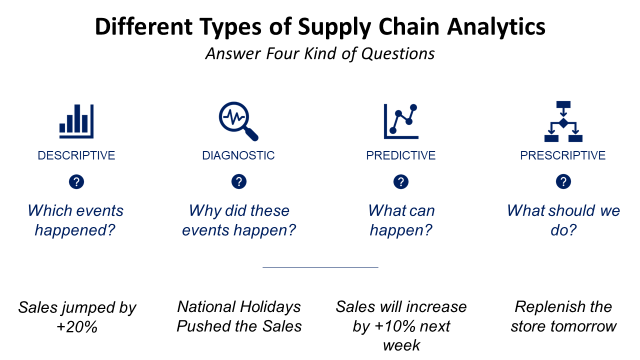
Now that you have the replica of your supply chain, you can play with the parameters and use data to perform.
Descriptive Analytics: monitor your processes with dashboards and visuals
Diagnostic Analytics: automate root cause analysis processes
- Logistic Performance Management Using Data Analytics
- Lead Times Variability and Supply Chain Resilience
Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics: add forecasting and optimization models into your digital twin to improve ordering rules or planning
- Machine Learning for Retail Sales Forecasting — Features Engineering
- Production Fixed Horizon Planning with Python
- Optimize Warehouse Value Added Services with Python
- Improve Warehouse Productivity using Pathfinding Algorithm with Python
- Machine Learning for Store Delivery Scheduling
For more details,
Your digital twin can be seen as a core model in which you can add models that solve specific issues.
About Me
Let’s connect on Linkedin and Twitter, I am a Supply Chain Engineer that is using data analytics to improve logistics operations and reduce costs.
If you’re looking for tailored consulting solutions to optimize your supply chain and meet sustainability goals, feel free to contact me.